 A dancer of any calibre can face pressures in the dance studio, from themselves, their peers and even their dance teachers. Pressures can take hold in many forms, such as healing after injuries, aspiring to create the ‘ideal’ dancing body shape and changes in the behaviour of dance teachers. Each has an effect on both your dancing and performance, hindering the creation and maintenance of a healthy mind and body, which is paramount to excelling in and enjoying dance.
A dancer of any calibre can face pressures in the dance studio, from themselves, their peers and even their dance teachers. Pressures can take hold in many forms, such as healing after injuries, aspiring to create the ‘ideal’ dancing body shape and changes in the behaviour of dance teachers. Each has an effect on both your dancing and performance, hindering the creation and maintenance of a healthy mind and body, which is paramount to excelling in and enjoying dance.
Often teachers can appear unfriendly and cold, not offering encouragement or help to young dancers. This can stem the enthusiasm a young dancer has for dance and can be detrimental to their progress as a dancer. A dance teacher’s decision to teach is a result of wanting to pass on their knowledge and aid other dancers, so erratic behaviour can often seem odd. They can be overly critical of your work however they usually have many students they are working with at one time, so try not to take their attitude personally.
While there are often jarring relationships with dance teachers, this can also occur on a personal level with yourself. Aspiring to be a thin waif-like dancer is unhealthy and can lead to dieting, starving and an eating disorder, which can ultimately be dangerous. Fortunately, there is now more emphasis on creating a strong body which is fit and ready to take on the challenges of dance, not likely to collapse afterwards. Teachers are now more focused on healthy eating to prevent disorders, and promote dance alongside wellbeing for the body and mind.
Similar pressures of this type on the self can also occur as a result of injuries, especially those that are slower to heal. As a dancer the mentality is to power through the class whatever the cost, due to lifelong mantras such as ‘the show must go on’ and ‘no pain, no gain’. An ethos of this sort is now becoming less common, as ultimately it is of the upmost importance that the body and mind heals following an injury.
Image courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
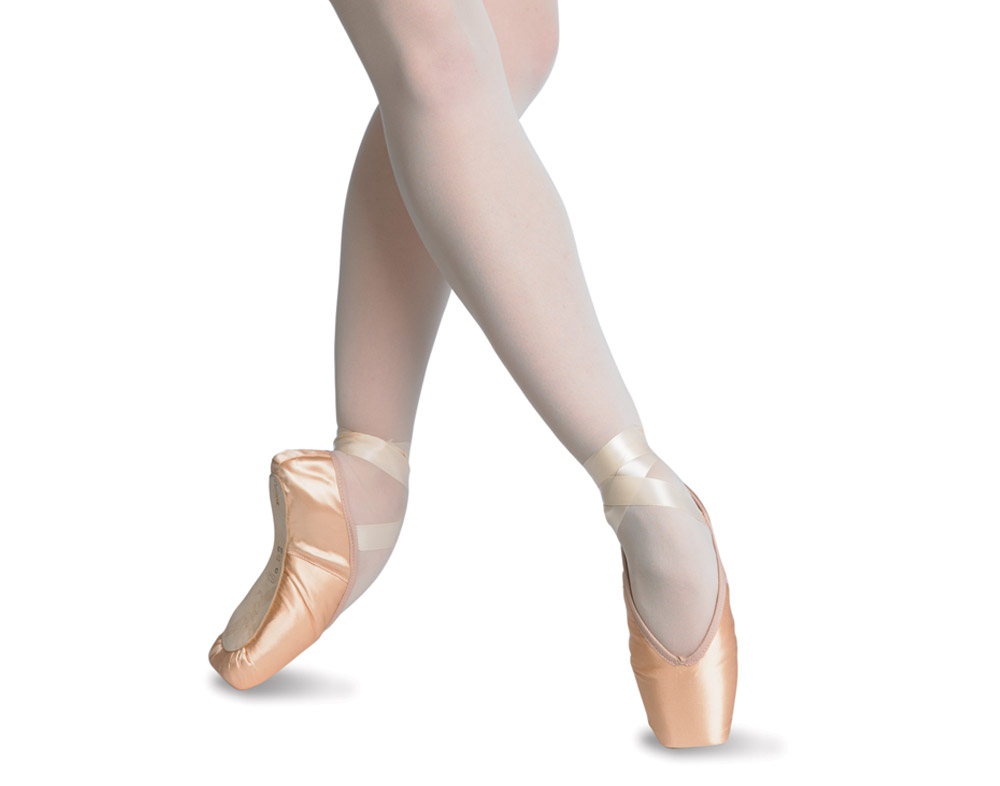
 There are many approaches to pointe training, and many reasons behind each of them. As an aspiring young dancer taking their first steps ‘en pointe’, you need training that will build up your strength whilst maintaining your technique, helping you to make a smooth transition onto pointe from ballet flats.
There are many approaches to pointe training, and many reasons behind each of them. As an aspiring young dancer taking their first steps ‘en pointe’, you need training that will build up your strength whilst maintaining your technique, helping you to make a smooth transition onto pointe from ballet flats. Dancers cannot just be fit to dance. Dance fitness in itself is not as wholesome as if the body undertook a wide range of physical activities to maintain fitness as a whole, whilst complementing that obtained through dance.
Dancers cannot just be fit to dance. Dance fitness in itself is not as wholesome as if the body undertook a wide range of physical activities to maintain fitness as a whole, whilst complementing that obtained through dance. You have successfully auditioned and booked your first professional dancing job! Whilst this is hugely exciting and a great achievement, don’t make first-time mistakes that could reflect negatively on you as a professional dancer… Some mistakes are common, some you only learn once you have been there and have done that.
You have successfully auditioned and booked your first professional dancing job! Whilst this is hugely exciting and a great achievement, don’t make first-time mistakes that could reflect negatively on you as a professional dancer… Some mistakes are common, some you only learn once you have been there and have done that. Dancing barefoot for modern or contemporary dance doesn’t come without its pitfalls – ballet dancers certainly suffer but that’s not to say contemporary dancers don’t too! Many dancers opt for socks, or their costume may demand them to be worn, however to fully feel the floor beneath you – and to move in response to that – requires barefoot dance. Despite this, dancers may still encounter problems along the way.
Dancing barefoot for modern or contemporary dance doesn’t come without its pitfalls – ballet dancers certainly suffer but that’s not to say contemporary dancers don’t too! Many dancers opt for socks, or their costume may demand them to be worn, however to fully feel the floor beneath you – and to move in response to that – requires barefoot dance. Despite this, dancers may still encounter problems along the way. Do you want to take your dancing to a professional level? As glamorous as it may seem, the life of a performer is a lot of hard work, pain and strict dedication to the goal. If you still wish to pursue a career in dance you must strive for it completely, as it requires a lot of passion and hard graft.
Do you want to take your dancing to a professional level? As glamorous as it may seem, the life of a performer is a lot of hard work, pain and strict dedication to the goal. If you still wish to pursue a career in dance you must strive for it completely, as it requires a lot of passion and hard graft. Even if dancers aren’t pointe novices, often there are still things to learn about caring for dance shoes, pointe shoes in particular. If you are new to pointe work for the new year, start as you mean to go on and ensure your shoes are cared for in the best possible way.
Even if dancers aren’t pointe novices, often there are still things to learn about caring for dance shoes, pointe shoes in particular. If you are new to pointe work for the new year, start as you mean to go on and ensure your shoes are cared for in the best possible way. Can you imagine a life in which you did not dance? This might be incomprehensible to some dancers, but for many, a break from the passion is exactly what they need.
Can you imagine a life in which you did not dance? This might be incomprehensible to some dancers, but for many, a break from the passion is exactly what they need.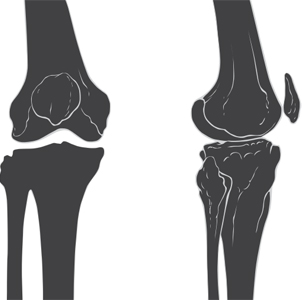 Do your knees hurt when you land from a jump, go downstairs, do grands pliés, or sit with them bent for long periods of time? “Jumper’s knee” could be the problem, a strain of the patellar tendon that runs from the lower kneecap to the upper shin. It is common in male ballet dancers and basketball players, who also jump a lot.
Do your knees hurt when you land from a jump, go downstairs, do grands pliés, or sit with them bent for long periods of time? “Jumper’s knee” could be the problem, a strain of the patellar tendon that runs from the lower kneecap to the upper shin. It is common in male ballet dancers and basketball players, who also jump a lot.