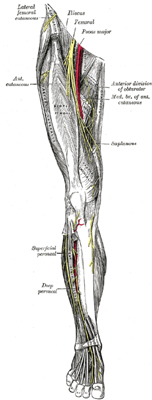
 The key principles of alignment will help to prevent dancers from getting injured; during ballet classes you may hear, “knees over toes”, “turn out from the hip” and “don’t curl your toes up” but the principles are the same for any dance discipline. Keeping your legs strong and aligned properly means you are using them correctly and have less chance of injury.
The key principles of alignment will help to prevent dancers from getting injured; during ballet classes you may hear, “knees over toes”, “turn out from the hip” and “don’t curl your toes up” but the principles are the same for any dance discipline. Keeping your legs strong and aligned properly means you are using them correctly and have less chance of injury.
When correcting alignment, begin with the hips. All rotation must come from the hip joints, not the knees, ankles or feet. The pelvis must be neutral, which is the safest position to work from. If the hip bones are forward, they are in an anterior tilt with an arched lower back; if they are titled backward the hips are in a posterior tilt, and tucked under. The knees should match the direction of the toes, which can be checked during pliés – the knees should track over the toes and the feet should not be rolling in.
It is important to keep the feet strong – imagine the foot is nailed to the floor, through the heel and each side of the ball of the foot. This reduces risk of injury and prevents the feet from rolling, which is especially important en pointe. The toes should be straight and lengthened on the floor which encourages articulation and secure, correct pointe work. When the dancer moves to demi pointe, ensure the work is not sickled by continuing to lift the arches. The weight should be centered over the first two toes to help strengthen the muscles on the outside of the ankle, and guard against ankle sprain.
Once the legs and feet are aligned correctly, it is important to keep your weight over your toes, and not to swing back into the heels. Don’t lift the heels, but ensure your weight is in the balls of your feet ready to move.

 In maintaining your health as a dancer it is important to consider all of the aspects of health which are equally as important as each other. For example nutrition through food and drink is used for the body’s every function, from muscle contraction to nerve impulses, with many nutrients taking on more than one job in the body. For instance, calcium is well known for being a hugely important part of bone health but is also critical for creating an electric impulse that travels down a nerve, and for allowing a muscle to relax after contracting.
In maintaining your health as a dancer it is important to consider all of the aspects of health which are equally as important as each other. For example nutrition through food and drink is used for the body’s every function, from muscle contraction to nerve impulses, with many nutrients taking on more than one job in the body. For instance, calcium is well known for being a hugely important part of bone health but is also critical for creating an electric impulse that travels down a nerve, and for allowing a muscle to relax after contracting. Regardless of your favourite dance discipline, it is important to maintain your practice in other dance forms to both complement and balance your training. Whilst one discipline may be concentrated on, it is beneficial both physically and mentally to take part in other dance forms other than your main interest.
Regardless of your favourite dance discipline, it is important to maintain your practice in other dance forms to both complement and balance your training. Whilst one discipline may be concentrated on, it is beneficial both physically and mentally to take part in other dance forms other than your main interest.
 The feet are important to any human being, in terms of posture, gait and movement. For dancers the feet are constantly put under pressure as dance relies predominantly on flexible, mobile and healthy feet. Despite this there are a few common foot injuries in dancers:
The feet are important to any human being, in terms of posture, gait and movement. For dancers the feet are constantly put under pressure as dance relies predominantly on flexible, mobile and healthy feet. Despite this there are a few common foot injuries in dancers: The benefits of turn boards can be debated. There are many aids, products and remedies for dancers on the market which help their training, however the pros and cons of turn boards can be identified easily. Seen in the dance film documentary First Position, it seems turn boards help dancers to master their pirouettes, improve confidence in turning and correct their spotting, balance and posture.
The benefits of turn boards can be debated. There are many aids, products and remedies for dancers on the market which help their training, however the pros and cons of turn boards can be identified easily. Seen in the dance film documentary First Position, it seems turn boards help dancers to master their pirouettes, improve confidence in turning and correct their spotting, balance and posture. Surprisingly many dance students find learning new combinations tricky and challenging. Of course the more you try to learn new exercises quickly the easier it becomes, but there are a few tricks to make it easier.
Surprisingly many dance students find learning new combinations tricky and challenging. Of course the more you try to learn new exercises quickly the easier it becomes, but there are a few tricks to make it easier. Fear backstage is common for at least 50% of performers, regardless of performance experience. More commonly known as “stage fright”, performance anxiety can be a constant problem or something that emerges over time.
Fear backstage is common for at least 50% of performers, regardless of performance experience. More commonly known as “stage fright”, performance anxiety can be a constant problem or something that emerges over time. After years of dance study you’re enrolled on a dance programme! Your goal may to become a professional dancer, to teach or study dance further, so make sure you work hard and dedicate yourself to your studies.
After years of dance study you’re enrolled on a dance programme! Your goal may to become a professional dancer, to teach or study dance further, so make sure you work hard and dedicate yourself to your studies. Many professional dancers rely heavily on false eyelashes, however this may not be a luxury for every dancer. It is possible grow, maintain and curl your lashes quickly and easily for that dramatic wide-eyed look often only achieved by false lashes.
Many professional dancers rely heavily on false eyelashes, however this may not be a luxury for every dancer. It is possible grow, maintain and curl your lashes quickly and easily for that dramatic wide-eyed look often only achieved by false lashes.