 The feet are important to any human being, in terms of posture, gait and movement. For dancers the feet are constantly put under pressure as dance relies predominantly on flexible, mobile and healthy feet. Despite this there are a few common foot injuries in dancers:
The feet are important to any human being, in terms of posture, gait and movement. For dancers the feet are constantly put under pressure as dance relies predominantly on flexible, mobile and healthy feet. Despite this there are a few common foot injuries in dancers:
Hallux Valgus and Bunions
The big toe tilts sideways towards the second toe and becomes painful, often developing bunion at its base. The pain is usually worse when wearing tight footwear, or when putting excessive pressure through the affected area, such as when on demi-pointe. The entire leg’s biomechanics are often involved: to manage the problem there are options of manual therapy, stretches and strengthening exercises for the feet, ankles, knees and hips. Failing this, surgery may be required.
Hallux Rigidus
This condition becomes apparent during full demi-pointe and is characterised by pain and reduced ability to achieve a 90 degree angle at the joint between the big toe and the rest of the foot. Forcing demi-pointes causes the joint surfaces to become irritated and bony spurs can develop. Half demi-pointes should be encouraged as the forces through the affected structures are then reduced. Cryotherapy (ice treatment), mobilisation and regular stretches can help in reducing pain and inflammation.
Plantar Fasciitis
Characterised by pain on the sole of the foot that is often worse in the mornings or after a strenuous exercise session. It is caused by an irritation and inflammation of the fascial covering of the sole of the foot and, in dancers, it is often linked to dancing for long hours on hard floors. Rest, cryotherapy, anti-inflammatories and manual therapy are all helpful in its management. Orthotics and splints can be used in chronic cases to help alleviate the symptoms.
Metatarsalgia
Characterised by pain over the ball of the foot. It is usually caused by years of overuse and overstretch of the ligaments of the toes; the associated joints become too unstable to sustain body weight and pressure which leads to metatarsalgia. Rest and cryotherapy are recommended, and metatarsal pads can be used to relieve pain and pressure, and strengthening exercises is encouraged.

 For many dance students, the summer spells summer schools and dance intensives. These summer training programmes are designed to push dance students further and give them another dance experience. They can vary in length, style and structure, but it is important to make the most of the programme while looking after your body.
For many dance students, the summer spells summer schools and dance intensives. These summer training programmes are designed to push dance students further and give them another dance experience. They can vary in length, style and structure, but it is important to make the most of the programme while looking after your body. While major injuries are devastating, it is often the smaller injuries which have more of an effect on a dancer’s wellbeing, such as being covered in bruises or burning the feet constantly. Dancers can become desperate for a cure, such as for cuts, split skin, blisters and bruises.
While major injuries are devastating, it is often the smaller injuries which have more of an effect on a dancer’s wellbeing, such as being covered in bruises or burning the feet constantly. Dancers can become desperate for a cure, such as for cuts, split skin, blisters and bruises. As a passionate young dance student, it can be hard to conceive of a life without dance. Perhaps you’ve been injured, or can’t get a job or even discovered a full dancing life just isn’t for you. You may be able to return to dancing, and if you do your body will not have forgotten, and you’ll be able to bring more to your dancing than previously.
As a passionate young dance student, it can be hard to conceive of a life without dance. Perhaps you’ve been injured, or can’t get a job or even discovered a full dancing life just isn’t for you. You may be able to return to dancing, and if you do your body will not have forgotten, and you’ll be able to bring more to your dancing than previously. Soft tissue therapy is a method used to assist dancers in building and maintaining flexibility and facility, as well as treating injuries, in keeping the body both strong and supple. Using soft tissue therapy aids dancers in reaching their potential: sometimes referred to as massage, the technique covers such a broad range of entities the term massage cannot encompass them.
Soft tissue therapy is a method used to assist dancers in building and maintaining flexibility and facility, as well as treating injuries, in keeping the body both strong and supple. Using soft tissue therapy aids dancers in reaching their potential: sometimes referred to as massage, the technique covers such a broad range of entities the term massage cannot encompass them. For most young children, dance class is a time to don the pinkest tights in town and join their friends in becoming fairies, soldiers and various other characters at the command of their teacher. It is only when children become a little older that ballet and dancing becomes a little more disciplined and structured. Instead of bouncing, bending and clapping there are pliés, tendus and lots of skipping. The focus may still be on having fun, but now works to encourage the ballet basics.
For most young children, dance class is a time to don the pinkest tights in town and join their friends in becoming fairies, soldiers and various other characters at the command of their teacher. It is only when children become a little older that ballet and dancing becomes a little more disciplined and structured. Instead of bouncing, bending and clapping there are pliés, tendus and lots of skipping. The focus may still be on having fun, but now works to encourage the ballet basics.
 For dancers, the correct nutrition for the body is of utmost importance for their performance in dance. Dancers are athletes combined with artistry, so they must think of themselves as athletes, and how athletes manage their food intakes or their nutrient and energy needs.
For dancers, the correct nutrition for the body is of utmost importance for their performance in dance. Dancers are athletes combined with artistry, so they must think of themselves as athletes, and how athletes manage their food intakes or their nutrient and energy needs.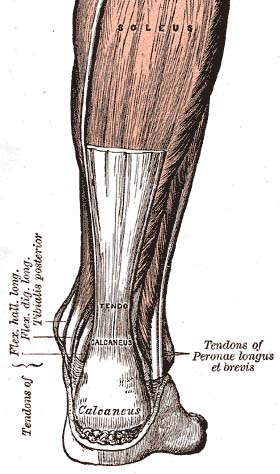 Are you blessed with long Achilles tendons, loose calf muscles and a deep plié? Count yourself lucky. Many dancers are desperate to increase the depth of their plié however, short of surgery, there is only so much change that can be made.
Are you blessed with long Achilles tendons, loose calf muscles and a deep plié? Count yourself lucky. Many dancers are desperate to increase the depth of their plié however, short of surgery, there is only so much change that can be made.